Google DeepMind Unveils 2.2 Million New Crystals, 380,000 Potential Game-Changers for Tech
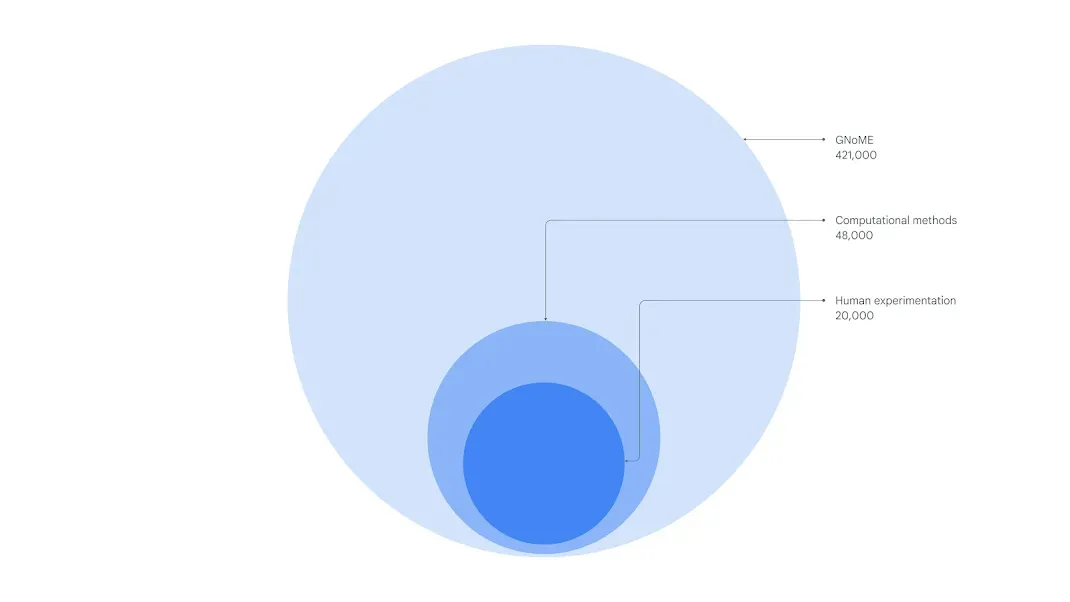
Prior to GNoME's innovation, material science faced hurdles in identifying viable crystals, often resorting to lengthy experimental methods.

Google DeepMind, researchers have introduced a cutting-edge deep learning tool, Graph Networks for Materials Exploration (GNoME), uncovering a whopping 2.2 million new crystals. Among these discoveries, 380,000 exhibit promising stability, potentially revolutionizing future technological advancements.
GNoME's unprecedented discovery, detailed in Nature, marks a monumental stride in crystal prediction, exploration, and synthesis. With an incredible acceleration in the process, this AI-powered tool has identified a multitude of potential materials that could redefine technology applications, including superconductors and advanced batteries for electric vehicles.
Notably, the tool's predictions have been confirmed by real-world validations. Researchers worldwide independently synthesized 736 of these newly discovered crystal structures, underlining GNoME's accuracy and groundbreaking potential.
Prior to GNoME's innovation, material science faced hurdles in identifying viable crystals, often resorting to lengthy experimental methods. However, this revolutionary tool's predictions, equivalent to 800 years' worth of knowledge, have changed the game by showcasing unparalleled scale and accuracy in material stability.
GNoME's discoveries are promising and expansive. It has surfaced over 52,000 new layered compounds akin to graphene, with transformative implications for electronics and potential superconductor development. Furthermore, it has revealed 528 potential lithium-ion conductors, indicating a substantial leap in enhancing rechargeable battery efficiency.
The tool's predictions align with strict stability criteria, yielding 380,000 materials that meet established standards. GNoME's innovative graph neural network (GNN) models leverage structural and compositional pipelines, hastening the discovery process by generating candidate materials resembling known crystals and employing randomized approaches based on chemical formulas.
With GNoME's extensive database now available to the research community, the potential for developing sustainable and transformative technologies appears closer than ever. These discoveries are expected to inspire new experiments and potential synthesis endeavors, potentially driving the next wave of technological innovation.
The remarkable findings from GNoME's AI-driven material exploration underscore the significant impact of advanced AI tools in reshaping material science, offering a glimpse into a future brimming with innovative possibilities.




